Gestational diabetes (GDM) is a condition that causes high blood sugar levels in pregnant women. It’s different from Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), diabetes in Nigeria has risen sharply in recent years. The 2011 IDF study estimated the prevalence of diabetes in Nigeria to be 4.04%, but a study conducted in a recently completed project found a gestational diabetes rate of 5.05 %.
Despite the high rate of diabetes and conception, at least one in ten women who have diabetes will not know about it before getting pregnant. While nine in ten do not experience symptoms, the risk of complications is higher for pregnancy and the baby.
Here are ten (10) other things to keep in mind if you are a pregnant woman with diabetes. They include:
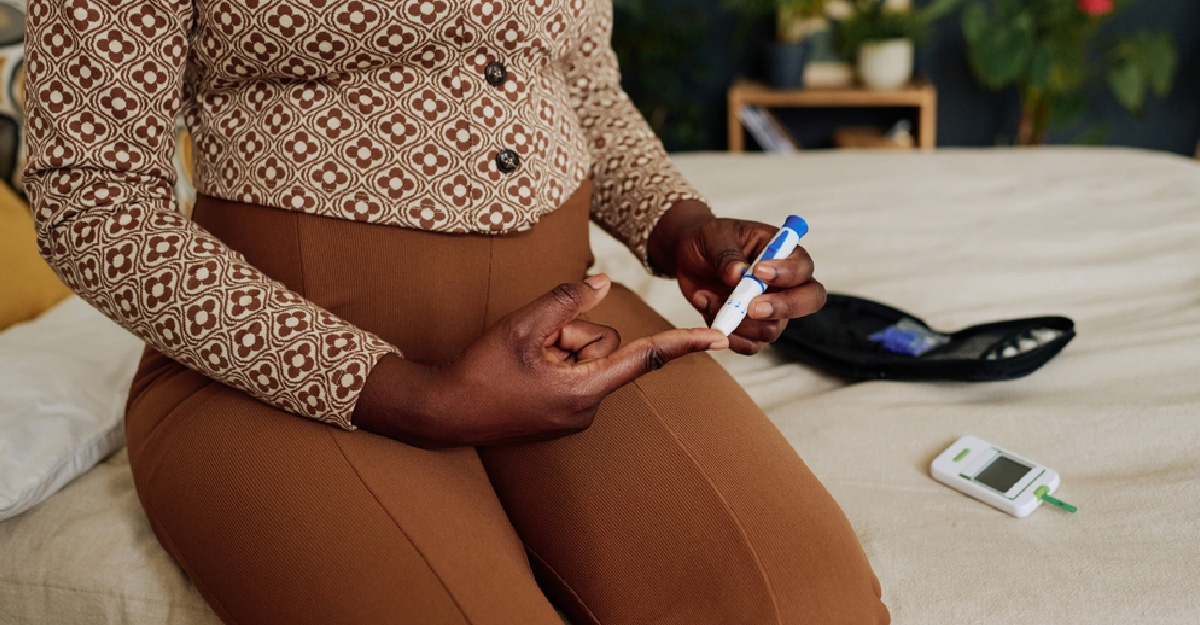
- You will want to test your blood sugar more frequently.
- Women who have diabetes have a higher risk of passing the disease on to their children.
- Diabetes can lead to babies being born prematurely because high blood sugar levels can cause the womb to contract.
- Healthy eating is essential for pregnant women with diabetes while controlling carbs and calories.
- Gestational diabetes can increase the risk of birth deformities.
- Medications women with diabetes take before getting pregnant can be dangerous for their babies if taken during pregnancy.
- Women with diabetes are more likely to develop high blood pressure and preeclampsia during pregnancy.
- Pregnant woman with diabetes needs to consult their doctors about how much physical activity is safe.
- During delivery, doctors will closely monitor your baby.
- Having diabetes doesn’t mean you can’t have a healthy pregnancy and baby.
Related: Here is all you need to know about the kidney function test
You will want to test your blood sugar more frequently.
When you’re pregnant, your blood sugar levels will rise. That’s normal for most women, but for women with diabetes, it can mean more frequent testing of their blood sugar levels.
Women who have diabetes have a higher risk of passing the disease on to their children.
Diabetic mothers have a higher risk of passing the disease to their children than women who do not have diabetes. The exact risk depends on the type of diabetes and the time of diagnosis. If your child is born with this condition, you’ll need to take special care of yourself and your baby.
Diabetes can lead to babies being born prematurely because high blood sugar levels can cause the womb to contract.
It can also make it harder for babies to get enough oxygen and nutrients through the placenta, leading to low birth weights. Babies born with diabetes may have other problems, including a higher risk of being born with birth abnormalities in their lungs or other organs.
Healthy eating is essential for pregnant women with diabetes while controlling carbs and calories.
A woman with diabetes needs to eat a healthy diet to ensure the baby is healthy. Eating right during pregnancy is vital for everyone, but it’s especially crucial for women with this condition.
A healthy diet should include carbohydrates, but if you have diabetes, measure them carefully because they affect blood sugar levels. The amount and type of carbohydrate in each food affect how much insulin your body will use to process it.
Gestational diabetes can increase the risk of birth deformities.
The risks of gestational diabetes extend beyond high blood sugar levels. Besides a higher chance of having a baby with health issues, women with gestational diabetes are also more likely to have:
- Birth deformities or preterm birth. Babies born with these conditions face an increased risk of long-term health problems, like heart defects and intellectual disabilities.
- Low birth weight (less than 5 pounds). A lower-than-normal weight at birth might mean that your baby isn’t getting enough nutrients in the womb, leading to physical growth and development issues.
- Being born with heart defects such as holes in the heart or abnormal connections between arteries or veins (arteriovenous fistula), specifically if these complications occur during the first trimester when the organs form.
Related: All you need to know about Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Medications women with diabetes take before getting pregnant can be dangerous for their babies if taken during pregnancy.
Pregnant women with diabetes should avoid the following medications:
- Antibiotics – metronidazole, nitrofurantoin, erythromycin
- Antifungals – griseofulvin, fluconazole, itraconazole
- Anti-inflammatories – ibuprofen and naproxen
Women with diabetes are more likely to develop high blood pressure and preeclampsia during pregnancy.
You may be more likely to develop high blood pressure, preeclampsia, and gestational diabetes while you’re pregnant. Preeclampsia is a condition that develops in the second half of pregnancy or the postpartum period. It involves high blood pressure and excess protein in the urine, leading to organ problems like kidney disease.
Pregnant woman with diabetes needs to consult their doctors about how much physical activity is safe.
As you are getting ready for pregnancy, it’s crucial to talk with your doctor about what types of physical activity are safe during pregnancy and how much exercise you need. The general guideline is that pregnant women do moderate aerobic exercises, like walking for at least 30 minutes.
Exercise can help keep blood glucose levels stable by increasing your body’s insulin sensitivity.
If you are unsure about certain activities during pregnancy or want more information on how physical activity benefits pregnant women with diabetes or any other health condition, ask a nurse practitioner or certified diabetes educator for suggestions on how best to stay healthy while expecting!
Related: 5 Reasons To Take a Pre-Wedding Screening Test Before Marriage
During delivery, doctors will closely monitor your baby.
Doctors will closely monitor your baby to ensure that it is safe and progressing normally. A pediatrician will ensure that your child is healthy by checking for hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), respiratory problems, jaundice, congenital anomalies, seizures, and other complications.
Having diabetes doesn’t mean you can’t have a healthy pregnancy and baby.
With diet and exercise, you can have a healthy pregnancy even if you have diabetes during pregnancy. It’s important to talk with your doctor about how best to manage your diabetes throughout your pregnancy to have the healthiest outcome for both mother and baby.
Related: 6 tests to secure your baby’s health during pregnancy
Conclusion
We’ve covered some of the extra complications present when a woman with diabetes becomes pregnant. There’s no need to panic, though it’s possible to have a healthy pregnancy and baby. Eating healthy, exercising regularly, and consulting your doctor will help you have a normal pregnancy. Read more on Diabetes. Click here to book a pregnancy health screening test.
6 reasons women need a high vaginal swab test
Related: Here is all you need to know about the kidney function test






No Comments