Occupational hazards are present in any workplace. They can be physical or chemical, and the effects can be short-term or long-term. Occupational hazards can cause harm to a person’s health and well-being and some cases, lead to death.
Some occupations are more hazardous than others, and some workers are more susceptible to hazards than others.
One way to address occupational hazards is by identifying them before they happen so that they can be avoided or controlled with appropriate safety measures, such as wearing protective gear or using gloves when handling hazardous materials. Continue reading to find out the steps.
Related post: Occupational Health And Safety In Nigeria: All You Need To Know
Types of Workplace Hazards
There are many types of occupational hazards, like physical, chemical, biological, and psychological. Some of the most common include:
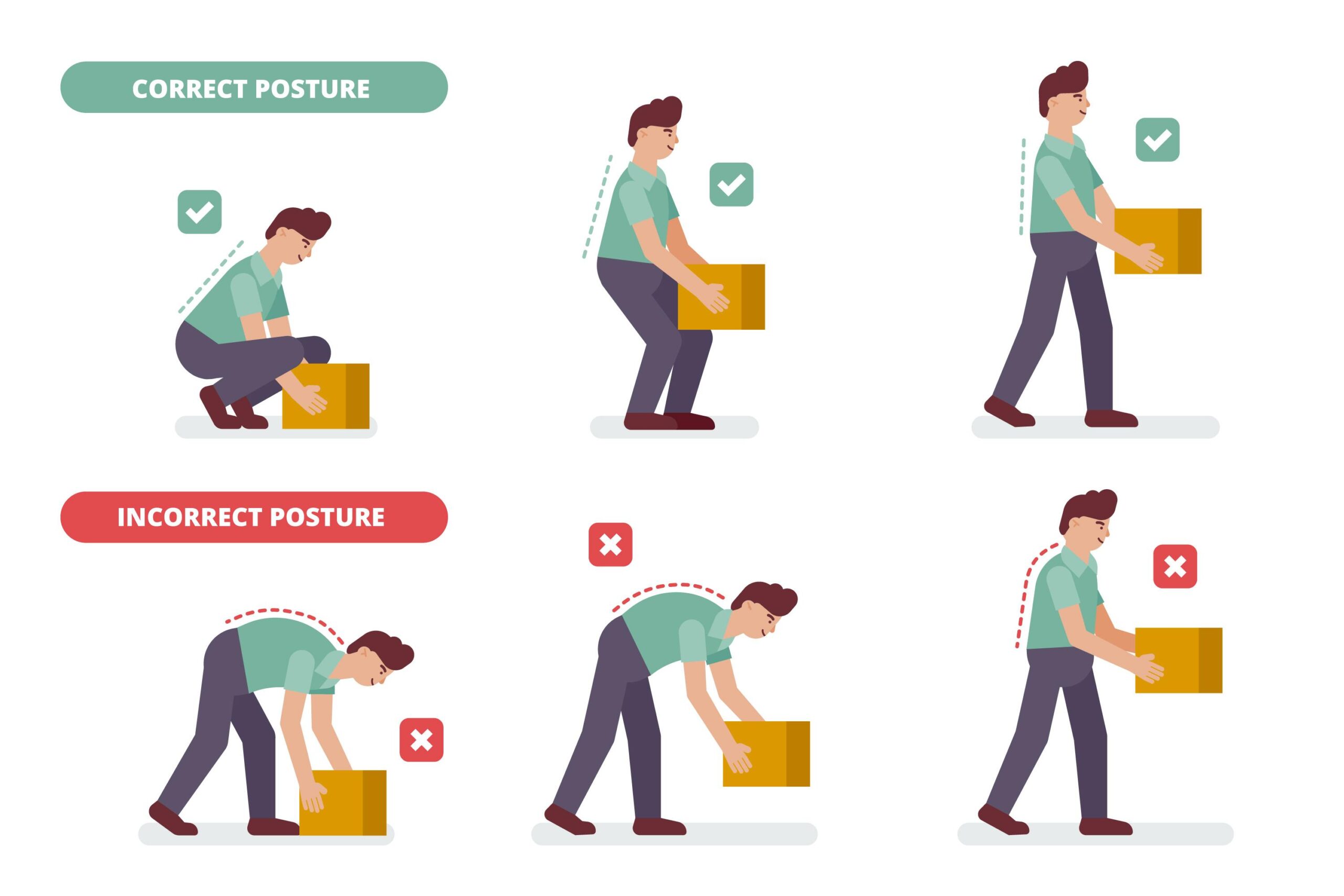
- Musculoskeletal hazards- Heavy lifting, awkward postures, prolonged standing or sitting, or performing work in motions cause this. The most common physical strain is carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS), occurring when the median nerve gets irritated due to pressure on the wrists or hands. CTS can be relieved with rest, wrist splints at night, gentle stretching exercises before starting work, and avoiding excessive wrist flexion while typing.
- Chemical hazards- It causes harm through direct contact, inhalation, ingestion, or absorption through the skin. Long-term health effects depend on the amount of exposure. Short-term effects may include irritation of the eyes and skin, a sore throat, headaches, nausea, dizziness, difficulty breathing, and heart palpitations. Long-term effects can be cancer, lung disease, nerve damage, and even death.
- Biological hazards- These are organisms or substances that can cause illnesses. It usually comes from animal or human sources. These include bacteria, viruses, fungi, and prions. A lack of proper handling means organisms can infect humans through ingestion, inhalation, or skin contact.
- Psychological hazards- The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) defines psychological hazards as conditions set by their potential for causing emotional or mental stress. These include, but are not limited to: sexual harassment, bullying, workplace violence, verbal abuse, low morale, high turnover rates, or lack of safety training.
- Slip and fall hazards- Slips, trips, and falls are the most common workplace hazards. Slips occur when a person’s foot slides on a surface that is not stable. Trips are when a person’s foot catches on an obstacle. Falls happen when a person loses balance and tumbles downstairs or over an object.
- Electrical hazards- Electrical hazards are issues in the workplace. The most common cause of worker injuries in the electrical industry is electrocution, which can occur when an employee touches an energized part of an electrical system without first disconnecting their body from the power source. Electrical accidents can also result from improper use of safety equipment, such as extension cords or power-saving devices that do not meet safety standards for use with electricity.
- Fire hazards- Many factors, such as faulty electrical wiring and equipment failure, can cause fire hazards. Flammable materials can also cause it by contacting an employee or visitor at work.
How to Identify Workplace Hazards
It is vital to identify hazards to control or eliminate risks. There are a few steps you can take to identify workplace hazards:
- Observe the workplace and look for any potential hazards.
- Ask employees if they have noticed any potential hazards.
- Review any safety or incident reports for any clues about potential hazards.
Once we have identified potential hazards, you can take steps to control or eliminate them.
Related post: The complete guide to Workplace Ergonomics
How Do You Prevent Hazards in the Workplace?
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) provides a set of guidelines to help employers prevent hazards in the workplace. By following these guidelines, employers can create a safe environment for their employees.
Some of the OSHA guidelines include:
- Providing personal protective equipment (PPE)
- Training employees on safety procedures
- Conducting regular safety audits
- Posting safety signs and warnings
Some other hazard prevention tips include:
- Cleaning up spills immediately
- Fixing loose wires and cords
- Using proper lifting techniques
- Storing chemicals properly
- Having a fire evacuation plan
By following these and other OSHA guidelines, employers can help prevent accidents and injuries in the workplace.
Related post: The complete guide to First Aid Training
Exit Route Planning
Exit routes are necessary for fire safety because they are a means of escape in the event of a fire. The routes should be well-lit, well-marked, and no more than one hundred feet from the workplace. It will help you to quickly and safely evacuate the area if necessary.
There are three things to keep in mind when planning your exit route:
- The route should be safe and free of obstacles.
- The route should be short and direct.
- The route should be well-lit and easy to see.
Keep these things in mind when choosing your exit route and practice it so that you can quickly evacuate the area in an emergency.
Related post: Workplace Emergency: Learn How To Create A Response Plan
General Safety Tips for Workers
- Be aware of your surroundings. Watch for any potential hazards that could cause injuries or accidents.
- Report any health concerns to a supervisor immediately.
- Never assume that a job is too easy or doesn’t require safety precautions. Safety always comes first, even on the simplest tasks.
- Keep your body as straight as possible when you work, maintain good posture at all times, and work with your feet shoulder-width apart.
In conclusion, hazards are present in all workplaces. Workplace hazards must be recognized and avoided. Several resources exist to help you identify and avoid dangers, including Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) guidelines and your company’s safety manual. If you need assistance identifying risks in your workplace, contact us today. As a company, our goal is to help you create a safe and healthy work environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the five hazards in the workplace?
Many hazards in the workplace can be hazardous to your health. Here are five of the most common ones:
Many hazards in the workplace can be hazardous to your health. Here are five of the most common ones:
- Exposure to chemicals
- Exposure to physical hazards
- Exposure to radiation
- Exposure to noise
- Exposure to infectious diseases
Related post: Workplace Safety: 9 Mistakes Companies Make
How can workplace hazards be controlled?
The five steps in the hierarchy of controls are:
- Elimination
- Substitution
- Engineering controls
- Administrative controls
- Personal protective equipment
How can we prevent hazards in the workplace?
Every workplace has different needs, but in general, there are five steps you can take to help keep your employees safe:
- You need to create a culture of safety where everyone feels comfortable reporting issues immediately, including supervisors and executives, if necessary.
- You need to have an emergency plan in place for every possible scenario that could happen at work, including natural disasters like earthquakes or hurricanes.
- You need to have a fire drill practice every month. Ensure everyone knows what to do if the situation requires an evacuation from the building (i.e., turn off all equipment).
- Setting up a communications policy that allows employees to report hazards and seek assistance to address workplace injuries or illnesses.







No Comments